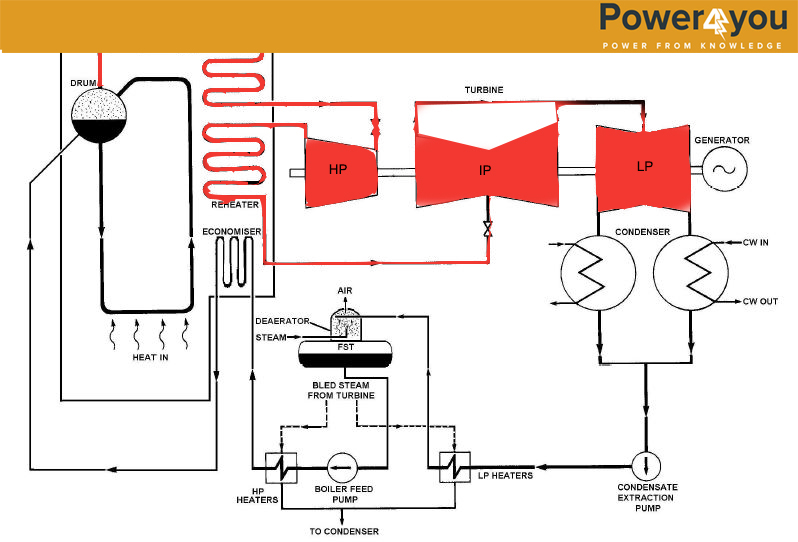
In order to generate electricity, we require mechanical torque and for the mechanical torque we require a fluid which will rotate the turbine, in thermal power plants to rotate the turbine we use steam as a medium. Steam is generated in boiler with the help of coal and water and after burning the coal, the heat generated is utilized to convert water into saturated steam.

(Steam Path in Boiler & Turbine)
Inside the boiler, there will be water-wall tubes in which the water is passing and we heat the water present inside the water-tubes by burning the coal at an elevated temperature. After absorbing that heat, that water is partially converted into steam in the water-wall tubes. This partially converted water and steam mixture goes into the boiler drum, where water and steam mixture is separated by drum internals. Then after the boiler drum, that saturated steam goes into the LTSH (low temperature super heater) or Primary super-heater which is present in the second pass of the boiler.
So a question arises why we need to send that saturated steam to super-heater?
Well, Super-heater serves three purposes-
- To extract heat from flue gases to minimize the wastage of heat in boiler
- To increase the enthalpy of steam so we extract more work in turbine.
- One more thing, if we dump that flue gases without extracting heat then after coming to atmosphere that gases heated the environment, which increase the temperature of earth.so it’s also put adverse effect on atmosphere.
After LTSH (low temperature super heater) that steam goes to the Platen super-heater or secondary super-heater which is present in the 1st pass. Platen name was given to this super-heater because of its plate type of structure. After passing from platen super-heater steam goes to final super-heater which situated in the 2nd pass. and after that the steam goes to HP(high pressure) turbine.
Primary super-heater (1st) and Final super-heater(3rd) are situated in 2nd pass and they take heat by convection heat transfer mode and the secondary or the platen super-heater takes heat by radiation heat transfer mode.In all super-heaters, many coils are present in which the saturated steam is passed. In different super-heaters, depending upon the designs, the number of coils may be different as per the design and the capacity of the plant. According to the plant capacity different number of super-heater are used which depend on the capacity of the plant. But all super-heater serves same function to extract heat from flue gases.
After HP Turbine, the steam again goes back to the boiler for reheating. This reheating phenomenon is to increase the efficiency of plant in order to extract more heat energy from the steam. After that steam goes to the primary re-heater it goes to the final re-heater. Where the steam temperature is again raised and then this steam goes back to IP(intermediate pressure) turbine. After expansion in HP(High Pressure) turbine and IP(Intermediate Pressure) turbine,the steam is fed to LP(Low Pressure) turbine. After expansion in LP turbine the steam pressure as well as temperature goes very low and its condensation starts afterwards .Finally this low energy steam is dumped in condenser.

(Super-heater Positions inside the Boiler)
Practically there is no limit on super-heating,but depending upon the metallurgy of the tubes it is limited to a certain value of temperature(e.g 540 Degree Centigrade) and in case of modern boilers a general trend is to employ minimum 3 stages of super-heater for better efficiency:
LTSH or Primary Super-heater
Platen Super-heater
Final Super-heater
Flow Pattern:
In super-heaters, most of the time the flow is cross-flow i.e. the steam after LTSH super-heater header goes to the platen super-heater header in cross pattern to evenly distribute the heat transfer. In super-heater safety valve is also present to prevent the over pressurization. if the super-heater is pressurized above its normal working pressure then safety valve opens and releases some amount of steam if not so then there is chance of bursting of tube because of high pressure.
As above mentioned that number of super-heater and types of super-heater is change according to design and capacity. there is also a divisional super-heater in some design. this super-heater present in between 1st and 2nd pass or we say where is the division between 1st and 2nd pass. Also in Chinese design there is a wall re-heater which structure is like wall. But both do same function as other super-heater and re-heater done.